Programmatic SEO Explained with 3 Case Studies (2024)

Programmatic SEO is a high-end strategy that tries to scale up the content creation and optimization with the power of automation and data-driven techniques.
Unlike traditional SEO, involving manual efforts to optimize a few pages, programmatic SEO enables dynamic creation and optimization of thousands or even millions of pages. It performs the best on websites targeting a large number of keywords—usually long-tail keywords—by generating vast amounts of content programmatically.
With Programmatic SEO, you’ll have the tools and knowledge to revolutionize your approach to search engine optimization and achieve better results than ever before.
Hugh Webb, How to Leverage Automation and Data Science for Better Search Engine Rankings
Before one gets into Programmatic SEO, it’s vital to understand what goes into basic Search Engine Optimization (SEO). This is how one would manipulate a website to make it readily visible and appear at the top of the search engine result pages. It thereby helps in receiving increased organic traffic for every higher ranking.
SEO mainly falls under three major categories:
– On-Page SEO: Optimizing Content and HTML source code of each page.
– Off-Page SEO: Getting Backlinks to the Website and social signals to increase authority of a website.
– Technical SEO: improvement in site structure, mobile-friendliness, and speed making sure that search engines are capable of crawling a site effectively and indexing it.
How Programmatic SEO Works
The following explanation are not in details but they are the main components:
1- The Core Concept
Programmatic SEO is at its heart an automated form of content-rich page creation using a data template.
It most commonly includes the following steps:
– Data Source: Information like product descriptions, user reviews, location data, or any other structured dataset that can fill out web pages.
– Templates: Pre-built page layouts that are able to be populated by data
– Automation Tools: Scripts, Content Management Systems (CMS), or custom software able to create and manage these pages in volume.
2- Data Powers Programmatic SEO
Data is the lifeblood of programmatic SEO. The key to success lies in finding or creating a structured data set that fuels meaningful content. Common sources of data include:
– E-commerce catalogs: Details of products, prices, ratings, reviews.
– Local business directories: Locations, contacts, business descriptions.
– Real estate listings: Details of property, locations, prices.
– Events databases: Event names, dates, and venues.
3- Scaling Templates
Programmatic SEO is reliant on templates. A good template design enables you to generate a high volume of pages that are all similarly structured and formatted, oftentimes with placeholders for dynamic data pulled from your dataset.
For example, a real estate site template might include:
– Title: “Buy [Property Type] in [City] – [Price Range]”
– Meta Description: “Find the best deals on [Property Type] in [City]. View listings with prices ranging from [Price Range].”
– Content: A table of property listings generated dynamically.
Combine this data with templates to create truly vast numbers of pages, optimized for long-tail keyword phrases. Most of the time, these long-tail keyword phrases have less competition in search results. You can study “How to Perform an Effective SEO Competitor Analysis” here.
Implementing Programmatic SEO
After getting familiar with the main components let’s review how to implement of programmatic SEO:
1- Keyword Research at Scale
At the heart of any SEO campaign is keyword research, and this is no different in programmatic SEO. However, the scale at which you will be doing keyword research is much larger.
The goal at this stage is to identify as many relevant long-tail keywords that your programmatically generated pages could rank for.
2- Data Collection and Structuring
After the identification of your keywords, the following step will be to collect and structure the data to populate your pages.
Typically, it will include the following steps:
– Web Scraping: Extract data from other external websites.
– APIs: Pull data from third-party services.
– Internal Databases: Use your company’s data, such as customer reviews or product information.
The data must be well-structured and probably within a relational database or JSON formatted to make integration with your page templates easy.
3- Content Generation and Automation Tools
To programmatically generate your pages, you’ll need automation tools or scripts that can pull in data from your dataset and place it within your templates.
Some common means include:
– Custom Scripts: These are written in languages such as Python and can be used to generate HTML files automatically.
– CMS Plugins: There are WordPress plugins , among other similar tools, which enable one to create content through data feeds.
– Headless CMS: These allow developers to create content repositories that can be accessed programmatically via APIs.
4- Dynamic Content and Personalization
One of the very strong features of programmatic SEO is creating dynamic content based on user behavior or any other variable. For instance, an e-commerce site is able to display a range of suggestions about products to a visitor based on his location or past behavior.
SEO Best Practices for Programmatic Pages
1- Unique and Valuable Content
The main problem with programmatic SEO, however, is Duplicate Content. Search engines are designed to penalize websites containing duplicate content. Therefore, it becomes essential that every dynamically generated page is unique and has value for its users.
That means strategies for uniqueness like:
– Content Spinning: modify text slightly so that it may not be considered a duplicate
– Content Enrichment: Add some unique data points, user-generated content, or other relevant multimedia like images and videos.
– Multiple Data Sources Consolidation: Combine data from multiple sources to create more enriched and fuller content.
2- URL Structure and Internal Linking
URL structure is crucial for SEO. Programmatic SEO often generates large numbers of URLs, so they must be clean and logical. For example:
– Use Descriptive URLs: Include keywords in the URLs, such as “/buy-homes-in-san-francisco”.
– Internal Linking: Programmatically link related pages to each other to improve navigation and distribute page authority.
3- Page Speed and Performance Optimization
Given the scale of programmatic SEO, ensuring that your pages load quickly is critical.
Techniques include:
– Lazy Loading: Load images and other resources only when they are needed.
– Caching: Use server-side caching to reduce load times.
– CDN Usage: Serve your content via a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to decrease latency.
Challenges and Pitfalls
1- Duplicate Content
The most common problem one encounters with Programmatic SEO is to avoid duplicate content. This might happen if your templates are too similar or if there’s not enough difference in the data between pages. Counter this by ensuring every page has enough uniqueness.
You can study Google Duplicate Content Policy here .
2- Thin Content
If you don’t have a sufficiently rich and diverse set of sources, there’s a risk that you’ll be left with pages that search engines would view as “thin” – in other words, not providing enough useful content. You can reduce this risk by augmenting your data with additional context or incorporating user-generated content.
3- Maintaining Big Websites
Programmatic SEO typically generates extremely large websites, often running into thousands of pages. Handling this kind of volume needs strong technical infrastructure in the form of efficient crawling and indexing strategies.
4- Algorithm Updates
Search engines are very active when it comes to updating their algorithms, many of which affect programmatic SEO strategies. Keeping pace with such updates and adapting your strategies in their light is the way to go.
Case Studies of Programmatic SEO
1- An online marketplace for short-and-long-term homestays and experiences in various countries and regions Airbnb:
With programmatic SEO, AirBnB dynamically generates landing pages for each of its thousands of listings targeting long-tail keywords such as “Vacation Rentals in [City]”.
Organic Search Traffic: 18.9M
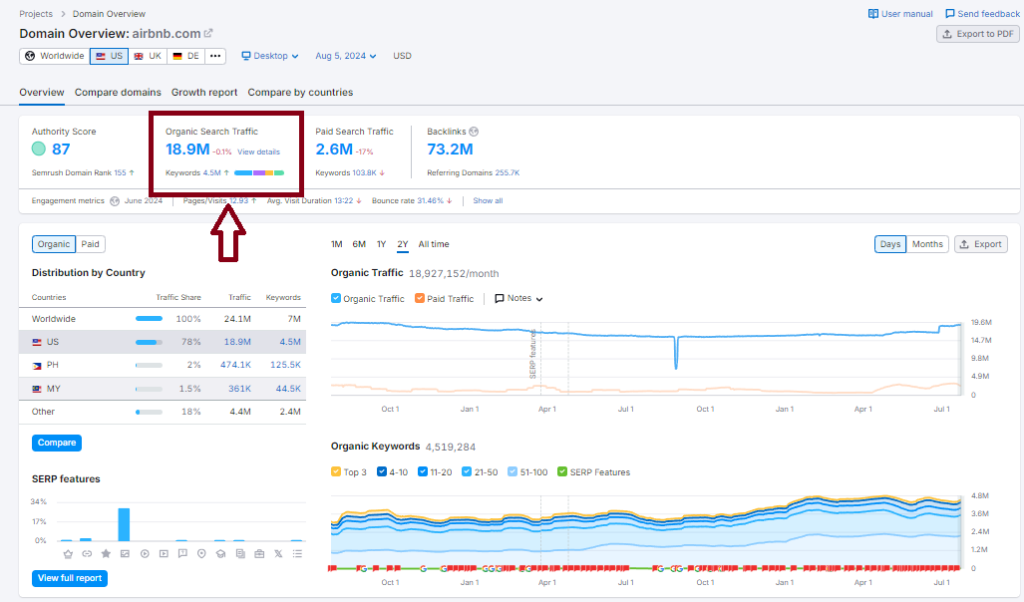
Keywords: 4.5M
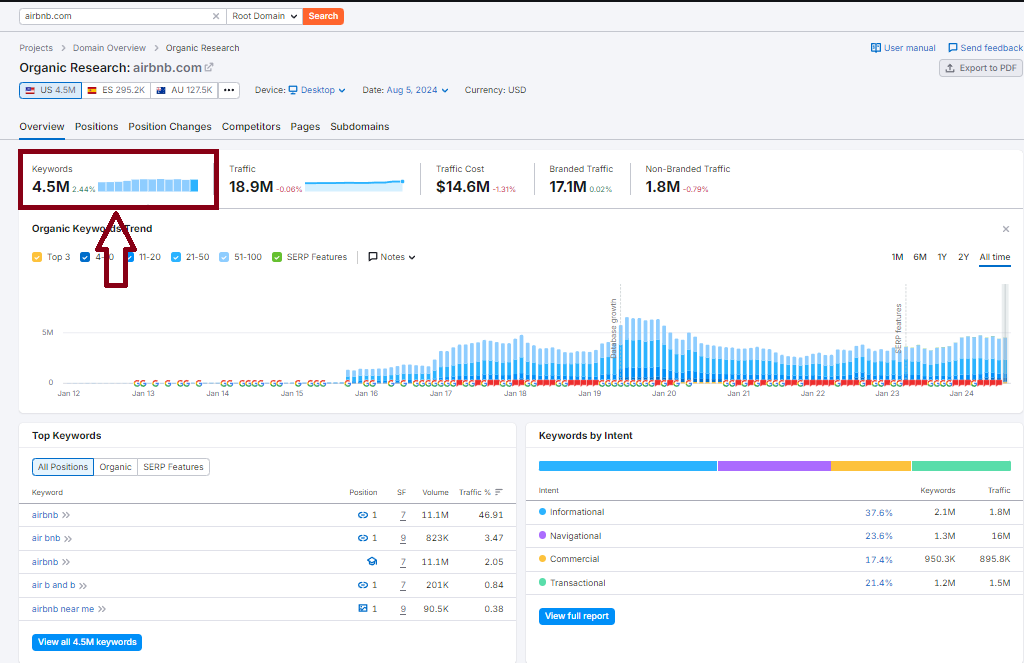
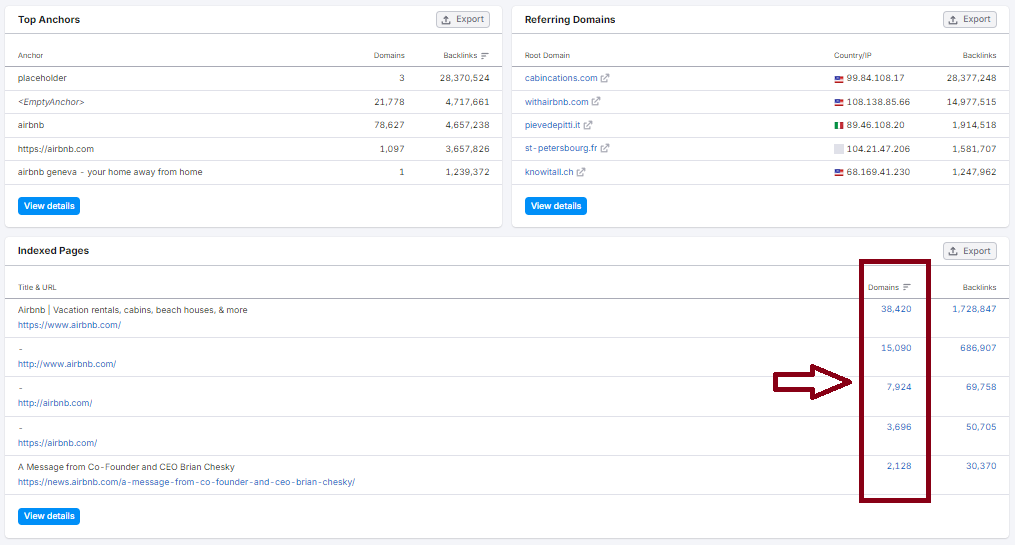
Indexed Pages: +40K
2- Croud-Sourced business reviews Yelp:
Yelp programmatically generates local business pages, subsequently ranking for a vast array of local search queries.
Organic Search Traffic: 143M
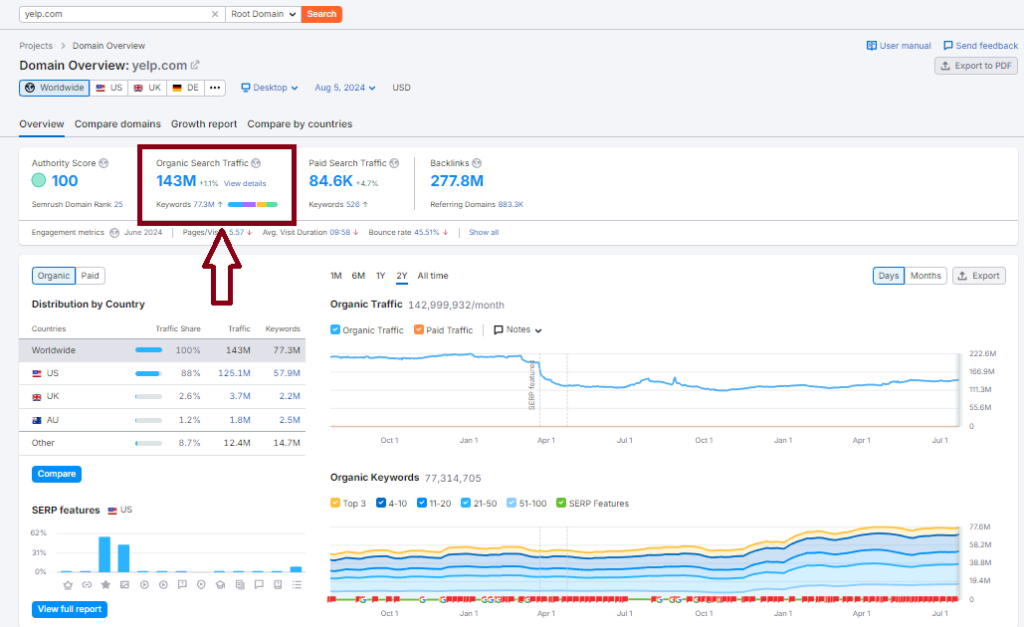
Keywords: +57M
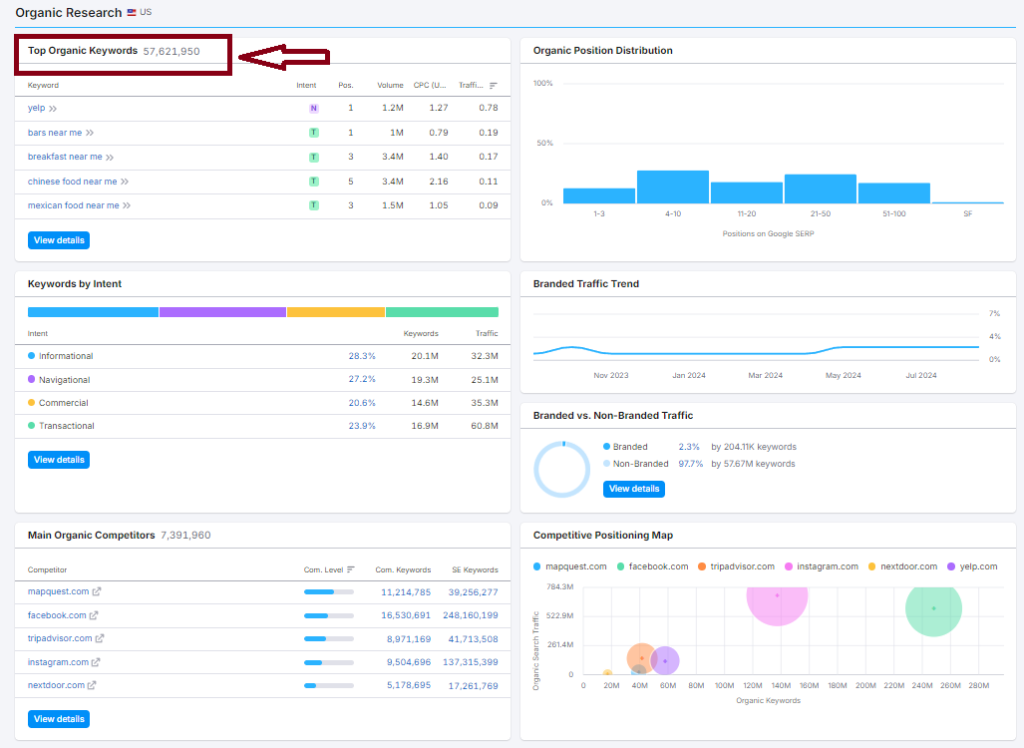
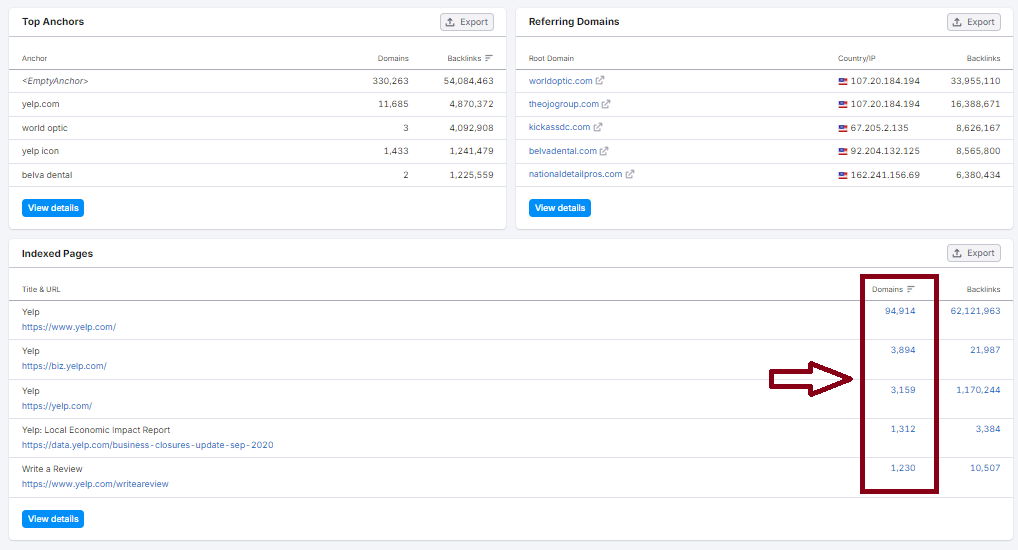
Indexed Pages: +95K
3- Online travel agencies, comparison shopping websites operator TripAdvisor:
TripAdvisor applied programmatic techniques to create pages on every possible keyword related to travel: from local attraction reviews to specific hotels.
Organic Search Traffic: +253M
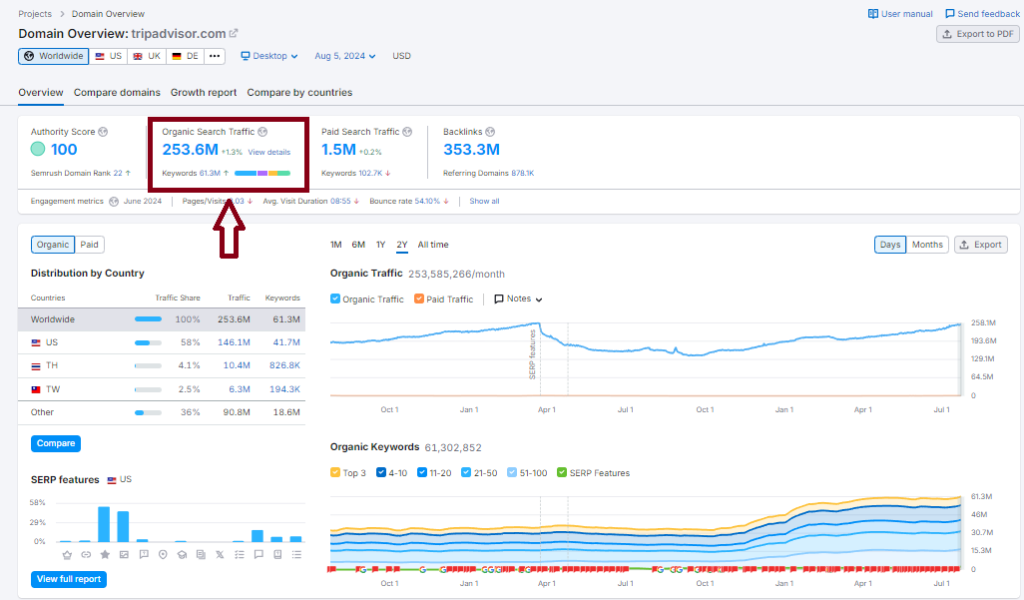
Keywords: +39M
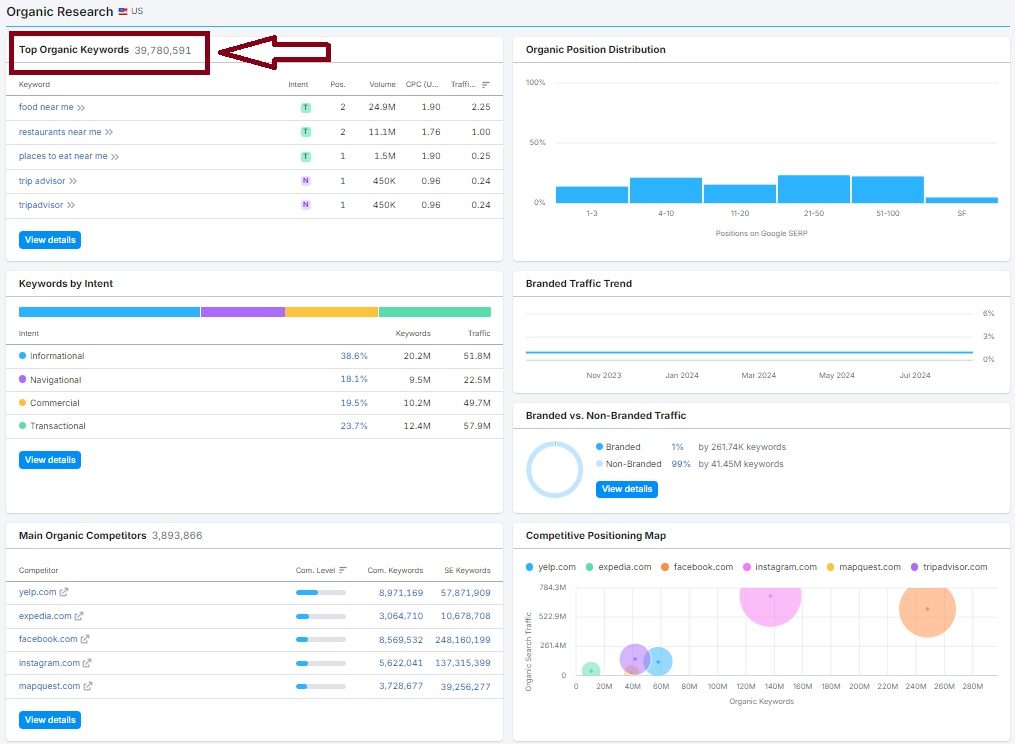
Indexed Pages: +52K
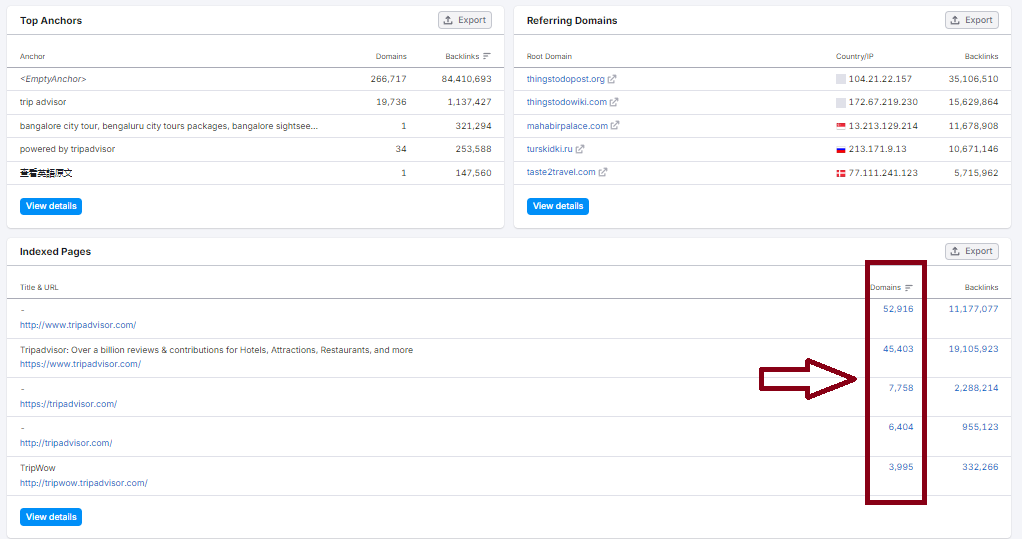
These examples highlight the importance of data richness, template variety, and continuous optimization to succeed in programmatic SEO.
Advanced Strategies and Future Trends
1- AI and Machine Learning in Programmatic SEO
The further development of programmatic SEO goes through the integration of AI and machine learning.
These technologies can:
– Analyze User Behavior: Dynamic content adjustment by user behavior data.
– Content Optimization: More engaging and human-like content can be generated with the help of natural language processing.
– Search Trend Prediction: Help in predicting future search trends and create content to rank for emerging keywords programmatically.
2- Voice Search and Programmatic SEO
With Voice Search increasingly becoming more mainstream, programmatic SEO must focus on question keywords and conversational keywords. There will be a growing need for optimizing pages for queries starting with “How,” “What,” “Where,” and other formats of questions.
3- Integration with Other Digital Marketing Channels
Programmatic SEO is increasingly being integrated with other digital marketing strategies, such as:
– Content Marketing: Programmatically generated content to fuel content marketing campaigns.
– Paid Search Campaigns: keywords identifying that perform well in organic search and use them in PPC campaigns.
– Social Media: Automatically sharing programmatically created pages on social media platforms.
Summary
Programmatic SEO is one of the most powerful ways to grow content creation and optimization. Challenges in it notwithstanding, it has the potential to drive tremendous organic traffic, which in turn makes this strategy very valuable either for large websites or those targeting a large number of niche markets.
In this regard, I would say that use of data, automation, and constant optimization within your programmatic SEO strategy will keep you at par with the ever-changing landscape of search engines. Growing and implementing programmatic SEO, remember that it means an interplay among creativity, technical know-how, and deep audience understanding.
References
- https://www.google.fr/books/edition/Programmatic_SEO_How_to_Leverage_Automat/HEfXzwEACAAJ?hl=en&kptab=overview
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchcontentmanagement/definition/content-management-system-CMS
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JSON
- https://wordpress.org/plugins/
- https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/gcp/how-to-build-a-website-on-google-app-engine-using-a-headless-cms-like-buttercms
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Article_spinning
- http://www.tripadvisor.com/
- https://www.airbnb.com/
- https://www.yelp.com/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google_Voice_Search
- https://ads.google.com/intl/en_us/home/resources/articles/what-is-paid-search/



